Data Exchange has become a strategic topic for organizations seeking to improve their operations, better address their markets, foster innovation, valorize their data, source data for their analytics, or more generally take an ecosystemic leadership in an increasingly interconnected economy.
With the sharp increase in data exchange volumes, operational challenges arise as organizations have to cope with several requirements and constraints, and respond to fundamental challenges:
- Trust building between data ecosystem participants
- Compliance with data regulations, applying to both data providers & acquirers and to the data intermediation service provider
- Security and data privacy
- Interoperability with any data infrastructure
- Performance and scalability of the data exchange operations
- Business flexibility to support multiple business models corresponding to the different Data Exchange use cases
In order to tackle these challenges, organizations need to rely on state-of-the-art Data Exchange technologies that address all domains in an integrated and consistent solution, delivering industrialized and future proof Data Exchanges.
This is why Dawex has focused, from the start, on developing an integrated technology interlinking thousands of functionalities dedicated to Data Exchange. Dawex customers can rely on the most complete and efficient Data Exchange solution to distribute, source or share data products, with full security and compliance to data regulations, and scale their operations in any business model.
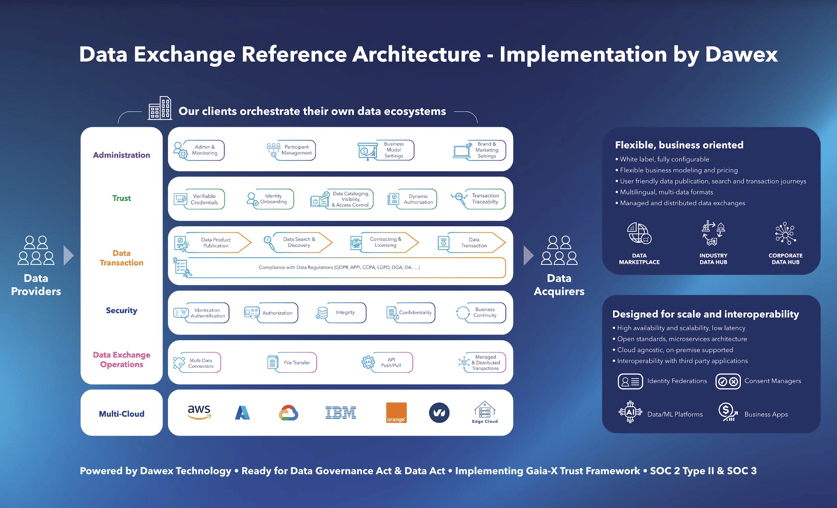
Players participating in the Data Exchange
- Orchestrator, also known as Data Intermediation Service Provider as defined in the European Data Governance Act (DGA): refers to the organization that provides services which aim to establish commercial relationships for the purposes of data sharing or data exchange between an undetermined number of data providers and data acquirers through technical, legal or other means. Orchestrators are customers of Dawex.
- Data Provider: The organization that grants access and usage rights for a data product to a data acquirer as the result of a data transaction. A Data Provider is a participant in the Data Exchange ecosystem.
- Data Acquirer: The organization that acquires access and usage rights for a data product from a data provider as the result of a data transaction. A Data Acquirer is a participant in the data data exchange ecosystem.
Administration
 Admin & Monitoring: Functionalities that allow the Orchestrator to configure white label, technical and functional settings that align with the orchestrator’s business strategy and compliance requirements. Monitoring features provide a real time view on participants activity, from consolidated reports to detailed participants, allowing a proactive and customized account management & support.
Admin & Monitoring: Functionalities that allow the Orchestrator to configure white label, technical and functional settings that align with the orchestrator’s business strategy and compliance requirements. Monitoring features provide a real time view on participants activity, from consolidated reports to detailed participants, allowing a proactive and customized account management & support. Participant Management: Allow the Orchestrator to manage the onboarding, vetting and revocation process for participants (data providers and data acquirers), to configure organizations profile settings, define & attribute roles, and manage sub groups or private groups.
Participant Management: Allow the Orchestrator to manage the onboarding, vetting and revocation process for participants (data providers and data acquirers), to configure organizations profile settings, define & attribute roles, and manage sub groups or private groups.  Business Model Settings: Through this set of capabilities, the orchestrator can define and manage business relationships with participants. It includes general conditions and pricing options such as subscription or commission fees.
Business Model Settings: Through this set of capabilities, the orchestrator can define and manage business relationships with participants. It includes general conditions and pricing options such as subscription or commission fees. Brand & Marketing Settings: These functionalities allow the Orchestrator to customize the participants experience: naming and branding management (white label), configurable onboarding experience, promotions tools for contents or successful use cases, visibility boosters, seasonal data events easy to deploy to increase engagement, and much more.
Brand & Marketing Settings: These functionalities allow the Orchestrator to customize the participants experience: naming and branding management (white label), configurable onboarding experience, promotions tools for contents or successful use cases, visibility boosters, seasonal data events easy to deploy to increase engagement, and much more.
Trust
 Verifiable Credentials: Implementation of a standardized framework for digital credentials that enables natural persons, organizations, ressources, data services or data products to present and exchange proof of their qualifications, attributes, or statements. These credentials are digitally signed, ensuring their authenticity and integrity. This technology plays a crucial role in building a trustworthy and interoperable data ecosystem.
Verifiable Credentials: Implementation of a standardized framework for digital credentials that enables natural persons, organizations, ressources, data services or data products to present and exchange proof of their qualifications, attributes, or statements. These credentials are digitally signed, ensuring their authenticity and integrity. This technology plays a crucial role in building a trustworthy and interoperable data ecosystem.
 Identity Onboarding: Specific capabilities that allow the orchestrator to verify that the data providers and data acquirers are indeed who they claim they are, through a vetting process. Data Exchange technologies are currently evolving to manage Self Sovereign Identities and Decentralized Identities systems (DID).
Identity Onboarding: Specific capabilities that allow the orchestrator to verify that the data providers and data acquirers are indeed who they claim they are, through a vetting process. Data Exchange technologies are currently evolving to manage Self Sovereign Identities and Decentralized Identities systems (DID).
 Data Cataloging, Visibility & Access Control: Trust is also about data providers being sure that the data they provide is only visible and accessible to the organizations that are permitted to. This requires many rigorous functionalities to set visibility and access policies for each of the data products published, and specifically to configure data access automatically or upon validation. Data cataloging features allow to consolidate and manage all these settings, to improve publication & search experiences.
Data Cataloging, Visibility & Access Control: Trust is also about data providers being sure that the data they provide is only visible and accessible to the organizations that are permitted to. This requires many rigorous functionalities to set visibility and access policies for each of the data products published, and specifically to configure data access automatically or upon validation. Data cataloging features allow to consolidate and manage all these settings, to improve publication & search experiences.
 Dynamic Authorization: For a higher level of Trust and Compliance, orchestrators or data providers may require that a consent is given dynamically (upon each data product access request) through a third party (i.e. a Consent management system). Dynamic authorization features allow to request such a consent at a granular level, data product per data product.
Dynamic Authorization: For a higher level of Trust and Compliance, orchestrators or data providers may require that a consent is given dynamically (upon each data product access request) through a third party (i.e. a Consent management system). Dynamic authorization features allow to request such a consent at a granular level, data product per data product.
 Data Transaction Traceability: Trust in Data Exchanges requires that the data provider and data acquirers can trace and monitor all data transactions that they have performed. This set of functionalities provides easy access to the data transaction history, and deep dive capabilities to audit specific transactions.
Data Transaction Traceability: Trust in Data Exchanges requires that the data provider and data acquirers can trace and monitor all data transactions that they have performed. This set of functionalities provides easy access to the data transaction history, and deep dive capabilities to audit specific transactions.
Data Transaction
 Data Product Publication: Set of capabilities that allow the data provider to configure, end-to-end, its data offering (data product or data service). It includes data product description, technical exchange settings (API or file mode, managed or distributed), licensing terms, pricing settings, among others. The range of capabilities to support any pricing or technical exchange scenario is very wide.
Data Product Publication: Set of capabilities that allow the data provider to configure, end-to-end, its data offering (data product or data service). It includes data product description, technical exchange settings (API or file mode, managed or distributed), licensing terms, pricing settings, among others. The range of capabilities to support any pricing or technical exchange scenario is very wide. Data Search and Discovery: These capabilities simplify and improve the experience of the data acquirer. Leveraging data offering metadata descriptions, it allows the data acquirer to search specific terms, conditions, filter results against tens of categories, and discover snapshots of the data products exposed.
Data Search and Discovery: These capabilities simplify and improve the experience of the data acquirer. Leveraging data offering metadata descriptions, it allows the data acquirer to search specific terms, conditions, filter results against tens of categories, and discover snapshots of the data products exposed. Contracting & Licencing: The data provider can fully configure contract and license terms for each data product he publishes. This is critical to provide full control over data usage after the exchange, in compliance with regulatory and business requirements.
Contracting & Licencing: The data provider can fully configure contract and license terms for each data product he publishes. This is critical to provide full control over data usage after the exchange, in compliance with regulatory and business requirements.  Data Transaction: The data transaction itself is the moment where data provider and data acquirer agree and validate the terms & conditions of the Data Exchange. The data transaction is supported by capabilities allowing the two parties to discuss, potentially negotiate, and validate the agreement. It is also the moment where financial terms of the transaction (e.g. prices) are agreed upon and settled. The data transaction is immutable, traceable by both parties, and must comply with applicable data regulations.
Data Transaction: The data transaction itself is the moment where data provider and data acquirer agree and validate the terms & conditions of the Data Exchange. The data transaction is supported by capabilities allowing the two parties to discuss, potentially negotiate, and validate the agreement. It is also the moment where financial terms of the transaction (e.g. prices) are agreed upon and settled. The data transaction is immutable, traceable by both parties, and must comply with applicable data regulations. Compliance with Data Regulations: Data transactions are subject to an increasing number of data regulations, such as GDPR or équivalent regulations outside Europe, Data Governance Act applicable in Europe as of September 23, 2023, or Data Act currently in the adoption process. Any Data Exchange technology has to provide the means for the orchestrator, the data provider and the data acquirer to comply with these regulations. This is done through a set of functionalities and processes ensuring that the regulatory requirements are met at each step of a data transaction.
Compliance with Data Regulations: Data transactions are subject to an increasing number of data regulations, such as GDPR or équivalent regulations outside Europe, Data Governance Act applicable in Europe as of September 23, 2023, or Data Act currently in the adoption process. Any Data Exchange technology has to provide the means for the orchestrator, the data provider and the data acquirer to comply with these regulations. This is done through a set of functionalities and processes ensuring that the regulatory requirements are met at each step of a data transaction.
Security
 Identification/Authentication/Authorization: a Data Exchange technology should provide the most advanced functionalities to ensure that identities are genuine, through standards such as MFA and SSO, together with RBAC for all user accesses.
Identification/Authentication/Authorization: a Data Exchange technology should provide the most advanced functionalities to ensure that identities are genuine, through standards such as MFA and SSO, together with RBAC for all user accesses. Integrity: Integrity is crucial in the context of Data Exchange since it ensures that the data being transmitted or shared remains unaltered and accurate throughout the process. By maintaining data integrity, organizations can trust the information they receive, uphold the reliability of their systems, and protect against potential threats or errors that may compromise the quality and trustworthiness of their data.
Integrity: Integrity is crucial in the context of Data Exchange since it ensures that the data being transmitted or shared remains unaltered and accurate throughout the process. By maintaining data integrity, organizations can trust the information they receive, uphold the reliability of their systems, and protect against potential threats or errors that may compromise the quality and trustworthiness of their data. Confidentiality: Confidentiality safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. Ensuring that data remains confidential is essential to protect individuals' privacy, business data and sensitive information. Without confidentiality, data may be vulnerable to breaches, espionage, or misuse, leading to significant financial, legal, and reputational consequences. Maintaining confidentiality is not only a legal requirement but also an ethical imperative, as it preserves trust and integrity in Data Exchange processes, allowing individuals and organizations to share information with confidence that it will remain secure and undisclosed to unauthorized parties.
Confidentiality: Confidentiality safeguards sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure. Ensuring that data remains confidential is essential to protect individuals' privacy, business data and sensitive information. Without confidentiality, data may be vulnerable to breaches, espionage, or misuse, leading to significant financial, legal, and reputational consequences. Maintaining confidentiality is not only a legal requirement but also an ethical imperative, as it preserves trust and integrity in Data Exchange processes, allowing individuals and organizations to share information with confidence that it will remain secure and undisclosed to unauthorized parties. Business Continuity: Business continuity ensures that critical data flows remain uninterrupted, even in the face of unexpected disruptions such as natural disasters, cyberattacks or system failures. Business continuity measures, including data backup, redundancy and disaster recovery strategies, help maintain the seamless flow of information, enabling organizations to meet their obligations, serve their customers, and uphold trust in Data Exchange, even during challenging circumstances. Without a robust business continuity plan, Data Exchange processes can be severely compromised, leading to data loss, operational downtime, financial losses and damage to an organization's reputation.
Business Continuity: Business continuity ensures that critical data flows remain uninterrupted, even in the face of unexpected disruptions such as natural disasters, cyberattacks or system failures. Business continuity measures, including data backup, redundancy and disaster recovery strategies, help maintain the seamless flow of information, enabling organizations to meet their obligations, serve their customers, and uphold trust in Data Exchange, even during challenging circumstances. Without a robust business continuity plan, Data Exchange processes can be severely compromised, leading to data loss, operational downtime, financial losses and damage to an organization's reputation.
Data Exchange Operations
 Multi-Data Connectors: To deliver true interoperability with any data infrastructure that may be used by data providers and data acquirers, the Data Exchange technology has to propose a wide range of connectors agnostic to the infrastructure or application layers. This allows to manage Data Exchanges in an open approach and build data ecosystems easily, connecting data fabrics and infrastructures from different vendors.
Multi-Data Connectors: To deliver true interoperability with any data infrastructure that may be used by data providers and data acquirers, the Data Exchange technology has to propose a wide range of connectors agnostic to the infrastructure or application layers. This allows to manage Data Exchanges in an open approach and build data ecosystems easily, connecting data fabrics and infrastructures from different vendors.  File Transfer: One of the options for Data Exchange is to share or distribute files. A set of capabilities allow the data provider to define precisely how he wants to manage this type of exchange. It includes access path settings, file update frequency, definition of the transfer mode (managed or decentralized). All these capabilities have to be integrated with policies settings, such as access rights.
File Transfer: One of the options for Data Exchange is to share or distribute files. A set of capabilities allow the data provider to define precisely how he wants to manage this type of exchange. It includes access path settings, file update frequency, definition of the transfer mode (managed or decentralized). All these capabilities have to be integrated with policies settings, such as access rights. API Push/Pull: The other option is to exchange data through an API access. The Data Exchange technology provides all options to set up the technical transaction. It can be done in push mode where the data provider’s API pushes data products to the data acquirer’s API or directly to the data storage infrastructure, at a frequency and conditions determined by the data provider. It can also be done in pull mode, where the data acquirer sends a request to the Provider’s API, and receives the resulting data.
API Push/Pull: The other option is to exchange data through an API access. The Data Exchange technology provides all options to set up the technical transaction. It can be done in push mode where the data provider’s API pushes data products to the data acquirer’s API or directly to the data storage infrastructure, at a frequency and conditions determined by the data provider. It can also be done in pull mode, where the data acquirer sends a request to the Provider’s API, and receives the resulting data.  Managed and Distributed Transactions: Whether it is done through file transfer or API push/pull, the Data Exchange technology has to allow the data provider to decide whether he wants to leverage the Data Exchange infrastructure to transfer the data (going through a Router gateway in API mode, or through a captive file in file mode), or to perform the exchange directly through peer-to-peer connectors linking its infrastructure with the data acquirer infrastructure.
Managed and Distributed Transactions: Whether it is done through file transfer or API push/pull, the Data Exchange technology has to allow the data provider to decide whether he wants to leverage the Data Exchange infrastructure to transfer the data (going through a Router gateway in API mode, or through a captive file in file mode), or to perform the exchange directly through peer-to-peer connectors linking its infrastructure with the data acquirer infrastructure.
All the above capabilities have to be provided to the Data Exchange players to ensure they perform compliant, secure, trusted, efficient and flexible data transactions. These capabilities represent thousands of different functionalities that need to be integrated in a comprehensive Data Exchange solution, delivering a seamless and simple experience to all players.
Dawex constant investment in Data Exchange technologies since years, bringing deep expertise and market knowledge into architectural and technical design, has resulted in the most performant and comprehensive Data Exchange technology in the market, successfully supporting a variety of customers with different models such as Data Marketplaces, Industry Data Hubs and Corporate Data Hubs.
